Ion Channel Target Screening
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through channel pores. Their functions include establishing resting membrane potentials, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by controlling the flow of ions across cell membranes, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels exist in the membranes of all cells and are one of the two major types of ion carrier proteins, and the other is ion transporters.
Research Project
1.HCN Ion Channels
Hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels, which are non-selective cation channels that can be regulated by voltage and cyclic AMP (Camp) , are important targets for the heart and central nervous system.
2.Ligand-gated Ion Channels
1)Study of Acutely Isolated or Cultured Neurons:
This study focuses on the effects of drugs on different neuronal types, including those from the cortex, hippocampus, medulla, and dorsal root ganglia (DRG). We concentrate on observing the behavior of these neurons under conditions of acute isolation and culture, which encompasses investigating neuronal apoptosis, cellular damage, and protective effects in hypoxic conditions.
2)Electrophysiological Studies:
Voltage-gated (Na, CA, or K channels, etc.) or ligand-gated (GABA, NMDA, AMPA, etc.) as well as action potentials, spontaneous postsynaptic potentials, screening of analgesics, and mechanistic studies.
3.Transient Receptor Potential(TRP)Ion Channels
TRP (transient receptor potential) channels are a class of channel proteins that are widely distributed in the peripheral and central nervous systems, and more than 30 TRP channel family members have been cloned in mammals so far.
TRP ion channels are closely related to a variety of sensory responses, including heat, cold, pain, stress, smell and taste, and are easily regulated by natural aromatic substances, which are the therapeutic targets of many diseases.

Table 1: TRP ion channel family
4.Calcium Ion Channels
Calcium channels exhibit high selectivity for Ca²⁺ permeation. The opening of calcium channels allows calcium ions to enter the cell, thereby generating specific physiological functions. Besides, Calcium channels are significant targets for pharmaceutical action and are closely associated with various conditions, including cardiovascular diseases, pain, and Alzheimer's disease.
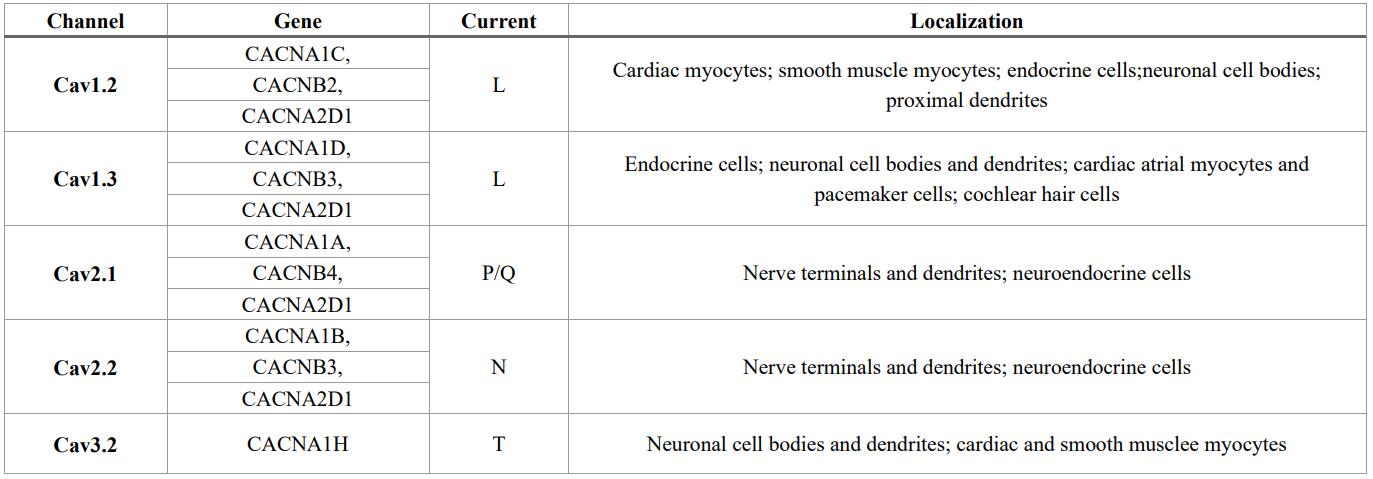
5.Potassium Ion Channels
The potassium channel family includes over 70 members, encompassing subtypes such as voltage-gated potassium channels (Kv), calcium-activated potassium channels (KCa), inward-rectifier potassium channels (Kir), and two-pore-domain potassium channels (K2P). Furthermore, Potassium channels are the most widely distributed type of ion channel, which is present in almost all living organisms and is closely related to the formation and regulation of the resting potential of cells.
LeadQuest Biotech has established nearly 40 human-derived stable cell lines expressing potassium channels, which are utilized for drug screening targeting potassium channels.
6.Sodium Ion Channels
Sodium channels are protein pores in the cell membrane that selectively allow the flow of sodium ions across the membrane. They are primarily voltage-controlled, playing a crucial role in maintaining the excitability of the cell membrane and the conduction of action potentials. Their physiological functions include: generation and conduction of signals in the nervous system; muscle contraction; formation and conduction of cardiac excitation; and gland secretion.
LeadQuest Biotech has developed both human-derived and murine-derived stable cell lines expressing sodium channels, along with primary cell testing methods, for drug screening targeting sodium channels.

*Nav1.5, Nav1.8, Nav1.9 are TTX-resistant sodium channels
7.GABAA Ion Channels
The GABA_A receptor is a transmembrane receptor composed of five subunits, which together form an ion channel. Each subunit contains four transmembrane domains, with both the N- and C-termini located outside the cell. These receptors are predominantly found on the post-synaptic membrane of neurons. GABA, the endogenous ligand of the GABA_A receptor, binds to the receptor, causing it to open its channel. This binding induces a conformational change in the receptor on the cell membrane, opening the channel pore and allowing chloride ions to flow through the ion channel, following the electrical and concentration gradients.
Since the reversal potential of chloride ions in most neurons is near, or slightly lower than, the resting membrane potential, activation of the GABA_A receptor can stabilize the resting potential or even hyperpolarize the cell, thereby weakening the depolarizing effects of excitatory neurotransmitters and reducing the likelihood of action potential generation. Thus, the GABA_A receptor primarily plays an inhibitory role, reducing neuronal activity.
LeadQuest Biotech has established GABA_A1-A6 channels expressing a variety of subunit combinations, offering drug screening services related to anesthesia, depression, and other conditions.
LeadQuest Biotech GABAA cell line









